Customer satisfaction, which is generally defined as conformance to requirements and fitness for use
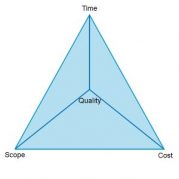
Quality is the fourth aspect of the most important triple constraint on any project. Project Quality Management ensures that Project and process remain on track and are progressing as per the baseline estimations and requirements.
Project quality management involves the procedures and practices that are used to determine and accomplish the quality of the deliverables of a project. Quality is what the customers or shareholders require from the project deliverables. It is the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements, decrease rework/costs, increase productivity/stakeholder satisfaction.
It encompasses all the activities that determine quality policies, purposes, and processes in an organization. Project quality management uses guidelines and strategies to successfully execute the organization’s quality management system. It supports consistently improving activities.
Grade relates to Features of the product, while Quality relates to Requirements of the product
Most importantly this is managements responsibility and should be undertaken by the whole team. PM is responsible for Project quality and Project Standards as a part of Plan Quality process but that cannot be much different both in practices or general expectations of Quality within Organization. OPA’s and EEF’s will affect you the most while dealing with the Quality. You need to be aware of some other concepts like Grade Vs Quality and Accuracy vs Precision while dealing with Quality.
Product satisfaction focuses the customer satisfaction whereas Project satisfaction deals with the Stakeholders;
Project Quality Management Processes
Quality Management Plan
The quality management plan is a major part of the project management plan that explains how the practical policies,
procedures and framework will be applied to accomplish the quality objectives. It describes the practices and means essential for the project management team to achieve the set of quality objectives for the project. The quality management plan can be formulated in official or unofficial, detailed or roughly framed. The elements of the quality management plan are primarily determined by the requirements of the project.
Tools and Techniques
- Process improvement plan covers all improvement practices involved
- Inspection planning adds up as a new technique as most tasks have some sort of testing, investigation, and reviews
- The plan outcomes update the RTM considering plan quality relevant new risks to risk register
Quality should be planned based on prevention rather then inspection led quality. Cost of Quality is a major parameter which outlines the organization’s preferences in terms of quality.
Manage Quality
Manage Quality refers to translating the quality management plan into practical quality practices that involve the organization’s quality framework into the task. The possibility of this process is prolonged beyond quality assurance without shifting the QA factors. The procedure of manage quality improves the likeliness of meeting the ultimate quality objectives. Also, it determines the inefficient processes and reasons for poor quality. It utilizes information from the control quality process to evaluate the overall quality status of the project to the stakeholders. The process audits the quality requirements to make sure that appropriate quality standards and functional definitions are used. The primary focus is to see how well the project adheres to the expected quality through audits and quality control tools. It is aimed at preventing any defects.
Control Quality
Quality control is the procedure of monitoring and recording outcomes of implementing quality practices to evaluate performance and suggest essential changes. In simple words, it’s the measurement of defects. The process identifies the causes of a failed process or product quality and suggests corrective actions. It validates the project deliverables to work according to the requirements defined by key stakeholders for final approval.
The manage quality is more concerned with process improvements and is in the Executing process group. Control Quality a process in Monitoring and Controlling process group and deal with end-product quality.
Quality should be planned, designed, and built-in, rather than inspected in.
Key Deliverables for Project Quality Management
Quality Management Plan
Quality management planning highlights the quality policies and processes relevant to the task for both project deliverables and project process. It defines who is responsible for what.
The processes in this knowledge Area of Quality Management helps avoid issues at a later stage of the project. Nobody wants to deliver a poor quality product which client/stakeholder/customer returns.
Quality Metrics:
Quality metrics are an important component of an efficient quality management plan. These measurements make sure that consumers receive acceptable goods or deliverables. Quality metrics are used to interpret users’ needs into satisfactory performance measures.
Quality Report:
A quality report refers to documentation that conveys information regarding the quality of a statistical good or process. It comprises of text and quality indicators that are recorded in a document or a database.
General Information: Seven Basic Tools of Quality
Though not any more specifically mentioned as part of PMBOK 6, it’s a good idea to know about the list of ‘Seven Basic Tools of Quality’;
- Cause-and-effect diagram
- Control Charts
- Flowcharting
- Histogram
- Pareto chart
- Run chart
- Scatter Diagram


