Project Cost Management
The Cost Management is among the most crucial project management knowledge areas and strongly connected with the Project Schedule Management as we will be using the same estimation techniques we have used there to estimate the cost and eventually budget.
Cost management should happen as early as possible in the project as it sets the policies for may other areas which deals with the costing on the project. All activities require a budget to be allocated to purchase tools, materials, and to cover human resource cost. There are multiple activities involve in a project that requires a budget to be allocated. This knowledge area is related to the management of the expenses and the budget of the project. It cannot happen in isolation – the project manager needs input from the project team and key stakeholders.

The process includes scheduling, estimating, budgeting, sponsoring, funding, handling, and monitoring costs so the project can be successfully completed within the approved budget. While working on cost, we need to review cost in multiple ways; Fixed vs Variable, Direct vs Indirect, Depreciations, Sunk Cost and etc.
Project Manager or Project Management teams basic responsibility is to complete the project within a specific time and approved budget and this where this knowledge area plays a vital role.
Project Cost Management Processes
Plan Cost Management (Planning)
The Plan Cost Management creates the framework, strategies, and procedures for how to estimate, manage and control costs. The process provides guidance on how costs are managed from project beginning to closure. This is the component of the Project Management Plan that shows how cost management processes should be carried out. The plan describes how project costs are prearranged, assessed, and controlled. It establishes the units of measure, level of precision and accuracy, control thresholds, reporting formats, organizational procedures links, and rules of performance measurement. This knowledge area in no way deals with pricing, something a buyer/supplier/contractor charges to customer for the services, material or time procured.
Estimate Costs (Planning)
The Estimate Costs refer to establishing an approximate monetary value to each project activity. The key benefit of the process is that it determines the amount of money required to complete project work. It’s a prediction of how much activity will cost upon accomplishment given the information. While estimating cost, it’s important to know whether you are estimating the direct project costs or indirect costs. To estimate costs, you must consider the project schedule to see which activities require what resources. The cost should be directly linked with WBS and objective of the SME should be to minimize the cost certainly not at the expense of Scope, Time and Quality.
You may be employing any of the following technique to estimate the duration of the tasks; though for all practical reason the best could be Bottom-up as this technique requires a team to think through the WBS thoroughly;
- Expert Judgement
- Top Down/ Analogous Estimation
- Bottom-up Estimates
- Parametric Estimates
- Three-point Estimates
Another important area which would add value to your analysis is the Basis of Estimates. This details how the cost estimate was derived, what were your assumptions and constraints, what is the confidence level of the final estimate and what are the expected ranges.
Estimates do get better over time as and when you more information about the project.
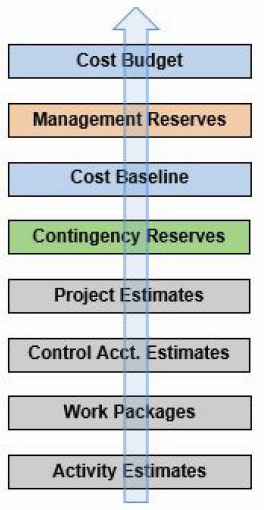
Determine Budget (Planning)
The Determine Budget is the procedure of combining individual activity or work package costs into the project budget. The key benefit is that it identifies the cost baseline against which project performance is measured. The process rolls up work packages into control accounts and control accounts into the project budget. This is where the cost baseline. Cost baseline is the time-phased budget, means when to spend money. Here another important item is Funding limit reconciliation; it addresses variance between funding limit and planned expenditure, which may require rescheduling of work to match the funding cycle. The S-Curve will help in understanding the project funding requirement. Funding on the project can be done through multiple ways, like self Funding, Bank Loans/Debts or Equity. Management reserves (overall project contingencies) are also allocated during this process.
Control Costs (Monitoring and Controlling)
The Control Costs refers to monitoring actual project costs against the cost baseline and managing changes to the cost baseline. The process permits the PM to detect cost variances early and take corrective actions to bring the project back on budget. It is important that over the period of time the allowed cost variance does go down because of tighter controls and less change request expectations. Any changes to the budget must be accepted through the Perform Integrated Change Control process. The Project Cost Control components include ensure timely application of change requests, issue cost-related change requests when required, monitor activity costs, and report cost performances to key stakeholders.
Project Manager or a Cost control manager may apply the earned value management to keep monitoring and in turn, keeping the cost under control. The process is based on three data Elements PV (Planned Value), AC (Actual Cost) and EV (Earned Value). This help in calculating 4 values through which project management team identifies the current progress/health of the project. CV (Cost Variance)and CPI (Cost Performance Index) to monitor and control Budget and SV (Schedule variance) and SPI (Schedule Performance Index) to manage the scheduling. The two Earned Value indices i.e CPI and SPI are important for Project Manager/Project Management team as CPI determines the relationship between planned and actual costs and SPI identifies about the efficiency of the team as they accomplished the work till the date of measurement.
Key Deliverables for Project Cost Management
Cost Management Plan
The Cost Management Plan establishes
- level of accuracy
- level of precision
- unit of measurement
- control threshold
- earned value rules of performance, reporting, funding and processes
Project Budget
Activity cost estimates + contingency reserves + work package estimates + contingency reserves + management reserve project.
Cost baseline
The Cost baseline informs you how much you should have spent at a given time period. It refers to the approved time-phased project budget. Any changes to the cost baseline must be permitted by the change control board.
Cost Baseline = Project Cost Estimates + Contingency Reserves
Cost Forecast
The Cost Forecast is the process that can be used to adapt cost planning according to consistently changing circumstances. For the cost to complete, the system identifies and values the activities based on the plan, forecast, and actual values in the network.
Further Readings

[pt_view id=”c356c37lza”]


One thought to “Project Cost Management – PMP/CAPM (PMBOK 6 – ECO 2019)”
Manage project portfolios, providing greater transparency over all existing work in progress. Cross-organisation breakdowns of current activity give a clear overview of what is happening, where, at any point.